fungi life cycle explained
To form n gametes n. Great yeast bud scars and pseudohyphae.
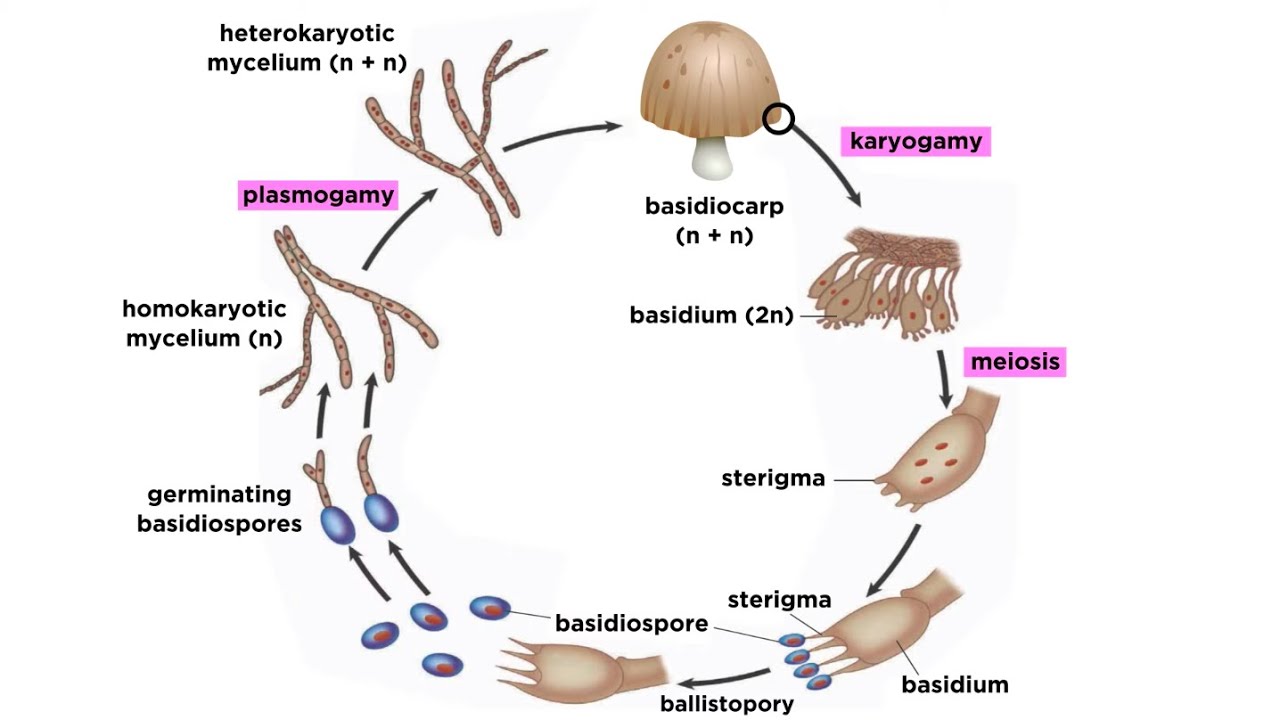
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube
The primary mycelium produced by the germination of basidiospore is of short duration.
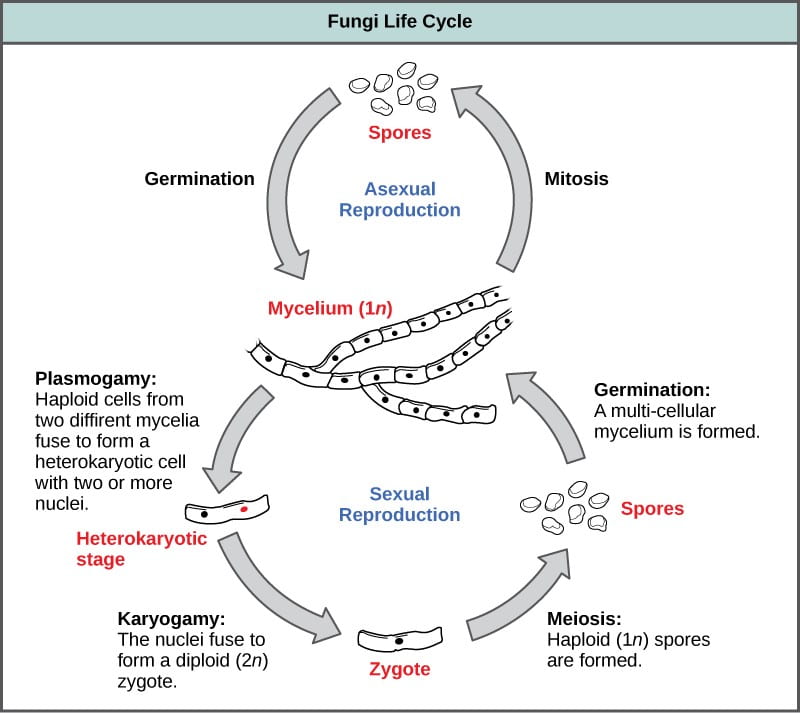
. Fungi cells have a nucleus and organelles like plant and animal cells do. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Single-celled fungi are called yeast.
You can think of the spore phase as both the beginning and end of a mushrooms life. Therefore dimorphic fungi possess two kinds of morphology in its life cycle. Life Cycle of Rhizopus.
Life cycle of fungi. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram. We can understand the meaning of the term dimorphic just by breaking it into two in which Di means two and Morphic means morphology or structure.
Identify and describe the key adaptations unique to fungi cell walls made of chitin and external digestion including morphological life cycle and metabolic traits. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. The mycelium is the root structure of a fungal speciesone stage of a fungi life span that branches throughout the Earths crust creating an underground interconnected network that connects.
Most fungi are microscopic but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need.
Some fungi alternate between single-celled yeast and multicellular forms depending on what stage of the life cycle they are in. It is haploid and either of plus strain or minus strain. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms.
The yeast produces hyphae strands and pseudohyphae. Fungal life cycles spores and more. The mode of asexrual reproduction.
The hyphae are septate. Some fungi are single-celled while others are multicellular. An Overview The fungi kingdom is an essential part of the Earths ecosystem and integral for its health and survival.
Describe the symbiotic relationship of fungi with plants and pathological relationships with other organisms. Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular. Dimorphic fungi can define as a type of fungi which has a dual life cycle.
They induce hypertrophic malformations of buds leaves twigs flowers and fruits producing. This fungus has a dimorphic life cycle with yeast and hyphal stages. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi.
The genus Taphrina old generic name Exoascus still in use by many authors contains several species which are very important pathogens. The pseudohyphae can give rise to yeast cells by apical or. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. Mushroom spores are tiny microscopic reproductive units that are produced by fungi as well as some types of plants and algae. Time which could partially explain Santas association with flying reindeer.
In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram. Edible and Poisonous Fungi Edible fungi Field mushrooms truffles honey rot Poisonous fungi Death Cap destroying angel. Life Cycle of Fungi.
While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. Soon as a result of hyphal fusions the primary mycelium becomes. Despite their diversity in many features the Ascomycetes possess certain common unifying characteristics namely the somatic body composed of a loose indefinite mass of septate mycelium.
Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding and many also have sexual. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. The cells contain oil globules vacuoles and are short and uninucleate.
With the elongation of the germ tube most of the mitochondria migrate into it and become concentrated near the tip. This is when mycelium comes together to form a knot near the surface of the soil which will soon develop into a primordia aka baby mushroom cute. A yeast-like fungus commonly occurring on human skin in the upper respiratory alimentary and female genital tracts.
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death. The first sign of an emerging mushroom is a hyphal knot. For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle.
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cellsMeiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates. This primordia is visible to the naked eye which means all the hard work is about to pay off. The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns.
Explain ecosystem services of fungi and human nutrition applications. Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of taphrina explained with the help of suitable diagrams.
Mushrooms create what is called a mycelium network.

Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Teelixir
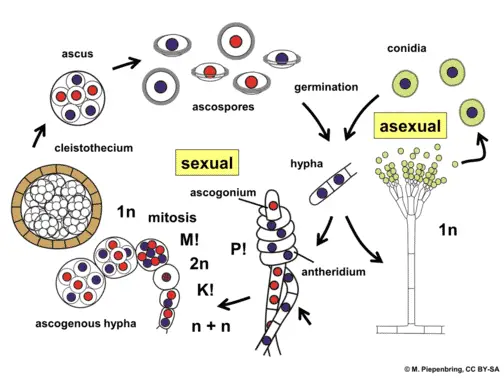
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle
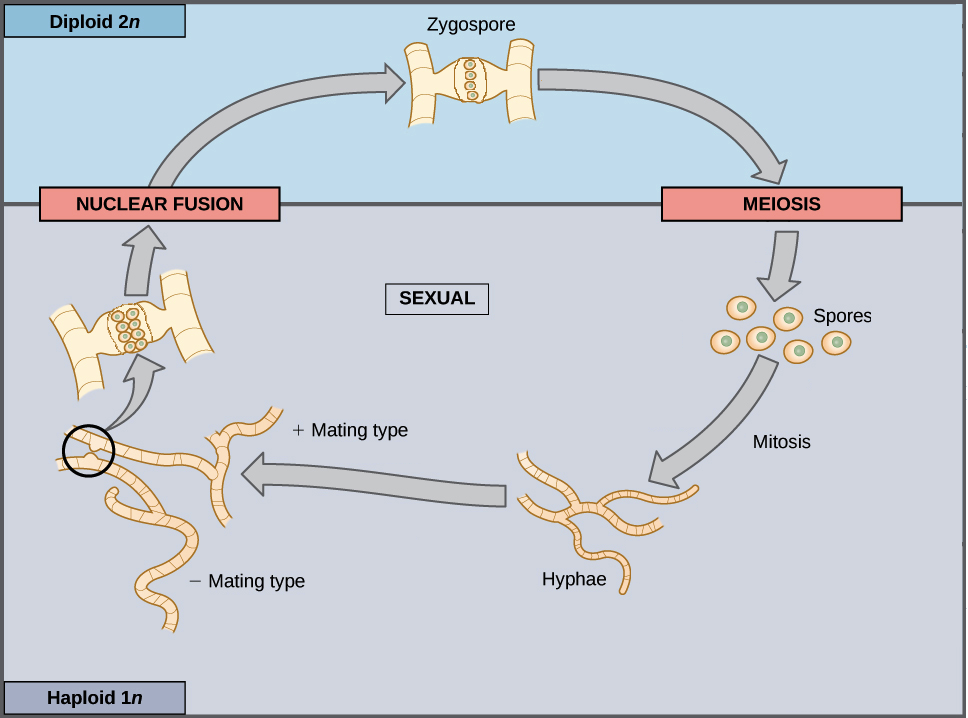
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Life Cycle Of Aspergillus And Suggested Localization Of Ribotoxins Download Scientific Diagram

